set 和 map 模板参数
STL容器中, set 和 map 虽然底层都是红黑树, 但是这两个容器的模板参数是不一样的, 在只考虑数据类型的情况下:
set 是 template<class Key>
map 则是 template<class Key, class Value>
很明显, 两种容器的模板参数数量都是不同的
要如何解决 相同的底层实现, 但是不同的模板参数呢?
有两种很简单粗暴的解决方法:
- 对set设计一个只有单个数据的红黑树; 对map设计一个 两个数据类型的红黑树
- 设计一个 两个数据类型的红黑树, 但是实现set时, 模板参数默认传0
但是 这两种方法 一个浪费, 一个粗暴, 都不是那么的优秀
简单分析一下 STL源码是怎么解决这个问题的:
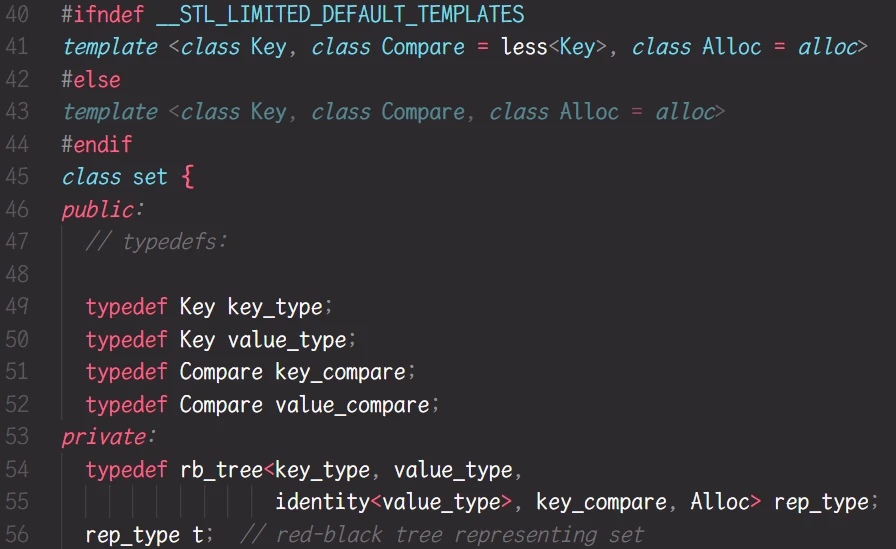
STL关于 set的部分源码:
可以看到, typedef红黑树的部分, 红黑树的模板参数传参是
<key_type, value_type>而
key_type和value_type其实都是Key
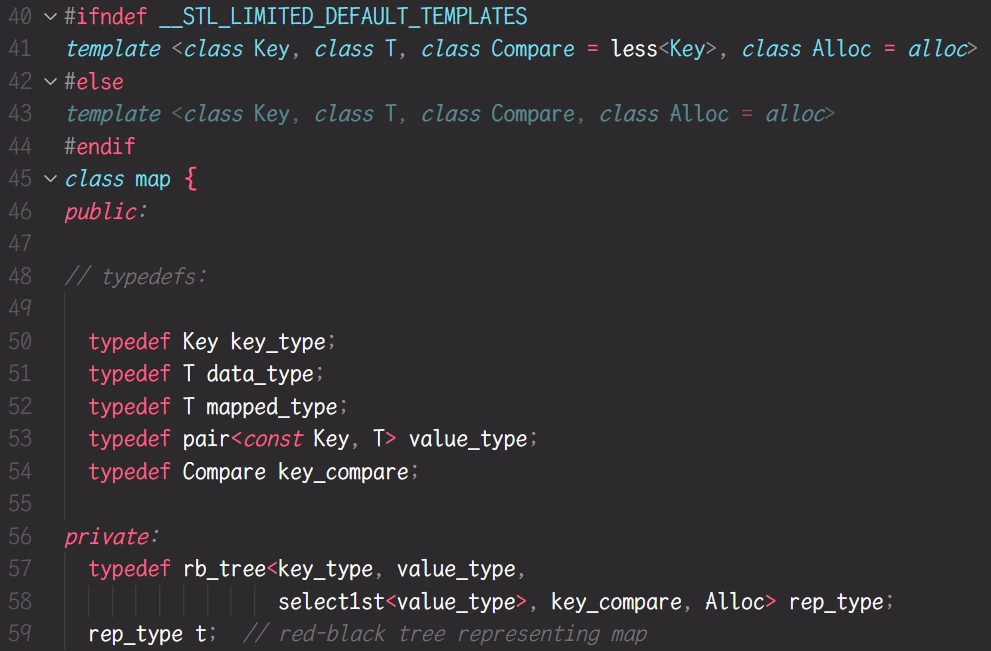
STL关于 map的部分源码:
map中 typedef红黑树的部分, 红黑树的模板参数传参 也是
<key_type, value_type>但是 map的
key_type是Key, 而value_type是pair<const Key, T>
只看 set 和 map 类型的部分源码基本看不出什么, 只能看出 STL实现两容器 底层使用的是有两个数据模板参数的红黑树
想要进一步看出具体的解决方案, 还要阅读一下 红黑树的部分源码
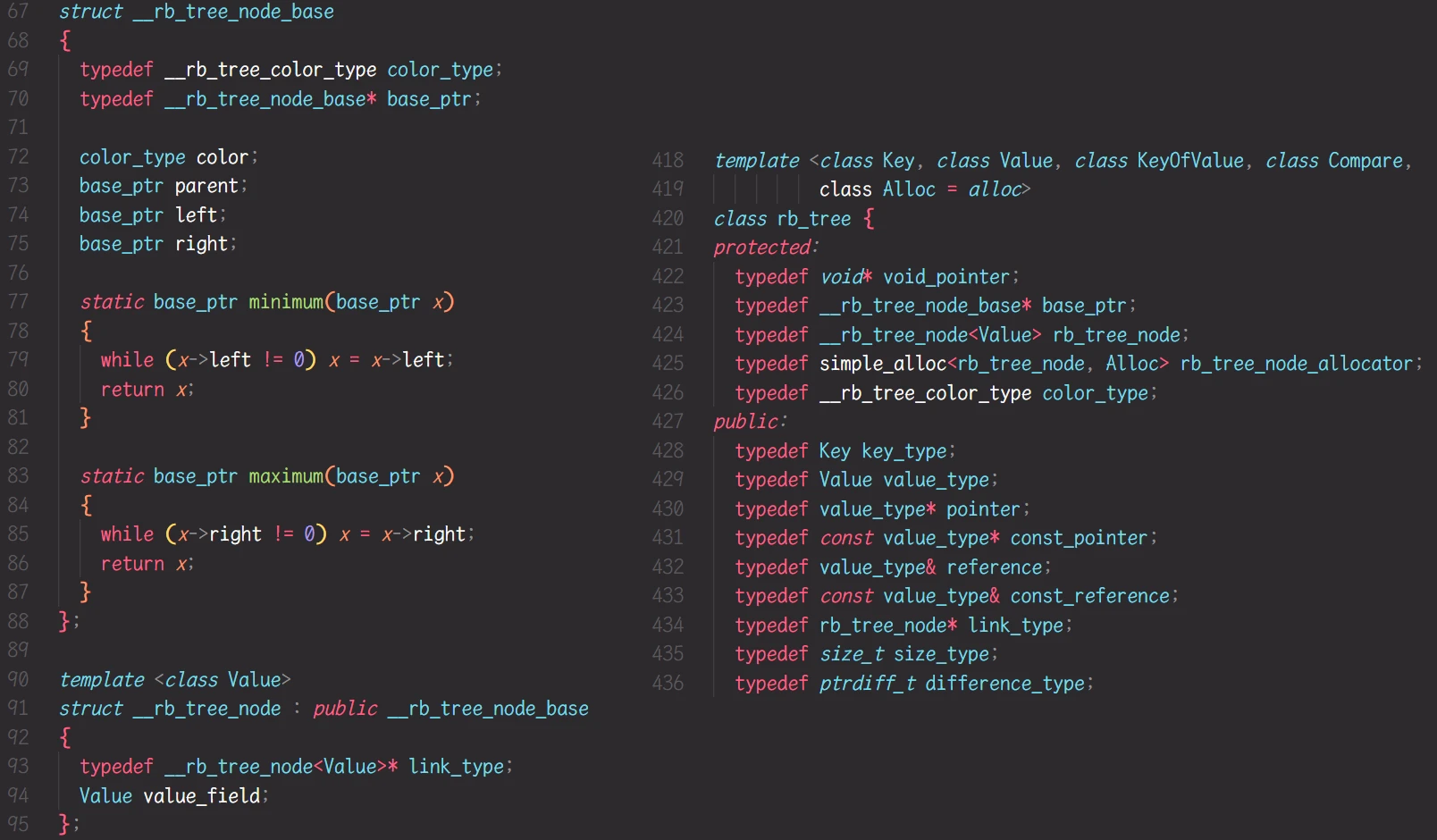
STL关于 红黑树的部分源码:
图中, 左半部分 是关于红黑树节点的部分源码; 右半部分 是关于红黑树结构的部分源码
阅读左半部分的源码, 可以发现 STL实现红黑树节点, 使用了继承:
将 每个节点都具有的部分: 颜色 父亲 左孩子 右孩子 定义为类
rb_tree_node_base; 定义另一个类 只拥有一个Value类型的成员变量, 其他继承于子类再阅读右半部分的源码, 发现
__rb_tree_node<Value> 被typedef为 rb_tree_node, 所以 红黑树的节点其实是__rb_tree_node<Value>类型的而 STL中 set 底层红黑树 传入的模板参数是
<key_type, value_type>, 且这两个类型相同 都是set的模板参数map 底层红黑树传入的模板参数也是
<key_type, value_type>, 但是 map中的 value_type 是pair<const Key, T>
总结一下:
STL实现set, set的关于数据的模板参数只有一个, 所以实例化 set 对象时 使用
set<Key>set 底层由红黑树实现, 红黑树的数据模板参数有两个, set 内部的 红黑树模板参数实际是
rb_tree<Key, Key>STL实现map. map的关于数据的模板参数有两个, 所以实例化 map 对象时 要
map<Key, T>不过 与 set不同, map底层 红黑树的模板参数实际是
rb_tree<Key, pair<const Key, T>>
简单的分析过 STL关于set map rb_tree的这一部分源码后, 其实就可以发现:
set底层红黑树模板 这样传参: rb_tree<Key, Key>, 红黑树节点中的数据类型是 Key; map底层红黑树模板 这样传参: rb_tree<Key, pair<const Key, T>>, 红黑树节点中的数据类型是 pair<const Key, T>. 所以, 其实不难发现 STL中 红黑树是 以第二个模板参数的类型作数据类型 来创建节点的
所以, 红黑树这样创建节点 就不需要再区分 set 和 map 数据模板参数数目不同的问题, 因为 即使容器的数据模板参数再多, 在调用红黑树进行模板传参时 也需要将所有数据类型整合到一个类型中 作为红黑树的第二个模板参数进行传参
红黑树的实现
STL中红黑树节点的数据类型是 红黑树的第二个模板参数的类型。所以, 此时实现的红黑树 相较于 上一篇文章分析红黑树时所写的红黑树结构 就会有一定的区别:
// 枚举常量, 表示 红 黑
enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode {
RBTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _color(RED) // 新节点默认为红节点
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _pLeft; // 节点左孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pRight; // 节点右孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pParent; // 节点父亲节点
T _data; // 节点数据
Color _color; // 节点颜色
};
template<class Key, class Value_type>
class RBTree {
typedef RBTreeNode<Value_type> Node; // 以 Value_type 作为节点类的模板参数 并 typedef
public:
bool insert(const Value_type& data) {}
private:
void rotateL(Node* parent) {}
void rotateR(Node* parent) {}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};红黑树节点类模板, 只有一个模板参数
红黑树类模板, 有两个数据类型模板参数, 但是 只用第二个模板参数 作节点的数据类型
红黑树节点数据的比较
红黑树是特殊的 二叉搜索树, 所以在插入数据时是一定会比较节点的数据大小的
对于基本的数据类型, 直接使用 >、< 等比较运算符就可以了
但是 对于复杂的类, 就比如 map 的节点数据类型 pair, 还可以直接使用 >、< 来实现目的吗?
pair类 数据大小的比较
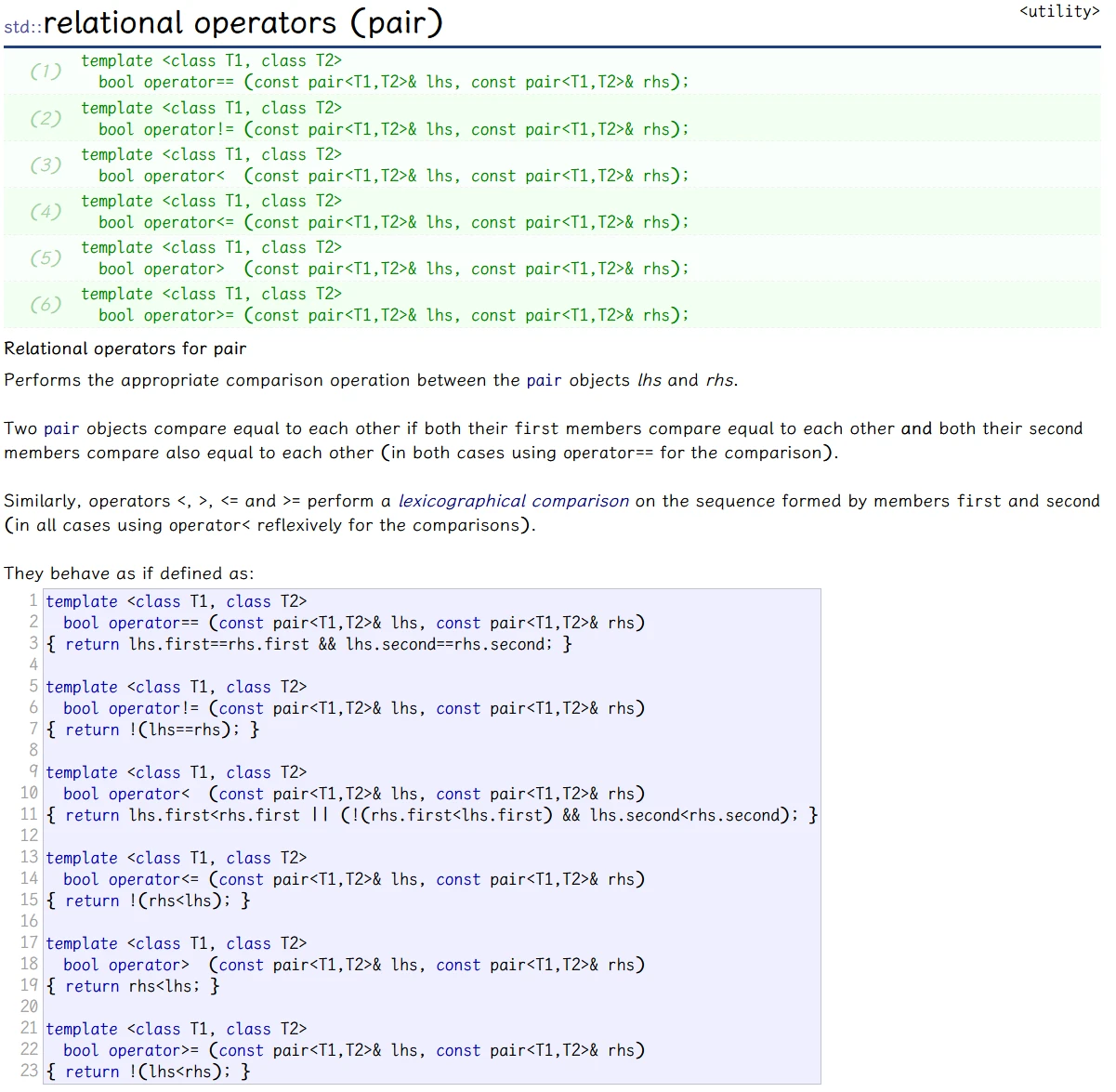
图中 蓝紫色部分的代码 就是 pair类中重载的比较运算符, 其中 == 和 < 运算符的功能是:
==:两pair对象的 first 和 second 都相等, 则为真<:左pair 的first 小于 右pair 的first 时或左pair的first 不小于 右pair的first时, 且左pair的second 小于 右pair的second时, 为真
可以发现, pair对象的比较 与 pair对象的两个成员变量 有关
红黑树第二个模板参数类型数据的比较
pair对象的比较 与 pair对象的两个成员变量都有关系, 但是 红黑树中节点的比较应该只对比 Key 的值, 而不对比 T 的值
所以 对set来说可以直接比较节点数据, 但是 对map来说不能直接比较节点数据, 因为 map节点数据的类型是 pair。
那么红黑树该如何设计, 才能兼容不同的容器呢?
其实可以效仿STL中的解决方法: 对不同的 容器 实现针对此容器的 取节点Key值的 仿函数
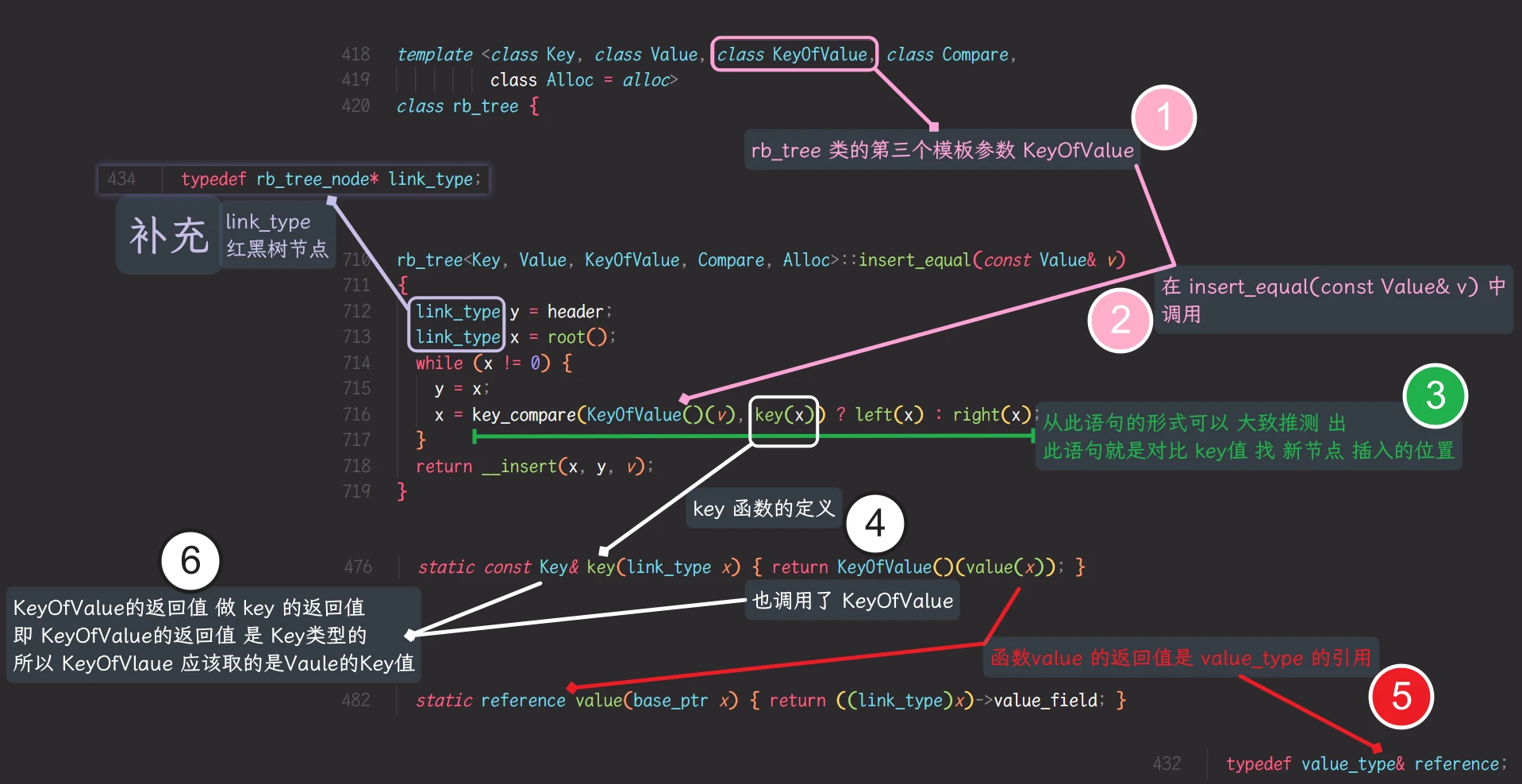
这是 在STL源码 分析的部分关于
取节点数据的Key值的仿函数的代码所以, STL源码中
红黑树的第三个模板参数就是 取节点数据的Key值的仿函数
仿函数需要在各自的容器中编写, 即 在Set中 写 取set的Key值的仿函数, 在Map中 写 取Map的Key值的仿函数
set 的取key值的仿函数:
template<class Key> class Set{ struct SetKeyOfValue { const Key& operator() (const Key& key) { return key; } }; };在 Set类 中定义一个 私有仿函数
map 的取key值的仿函数:
template<class Key, class Value> class Map{ struct MapKeyOfValue { const Key& operator() (const pair<Key, Value>& kv) { return kv.first; } }; };
Set、Map结构 及 底层红黑树插入实现
既然 Set和Map的底层红黑树 需要使用仿函数取对应的 key值, 所以 此时的红黑树 插入节点时, 无论是找位置还是调整节点 都需要使用仿函数来操作:
// 枚举常量, 表示 红 黑
enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode {
// RedBlackTreeNode 红黑树节点
RBTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _color(RED) // 新节点默认为红节点
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _pLeft; // 节点左孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pRight; // 节点右孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pParent; // 节点父亲节点
T _data; // 节点数据
Color _color; // 节点颜色
};
template<class Key, class Value_type, class KeyOfValue>
class RB_Tree {
typedef RBTreeNode<Value_type> Node; // 对节点类型进行typedef
public:
bool insert(const Value_type& data) {
if (_root == nullptr) {
// 树为空时, 插入新节点
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_color = BLACK; // 根节点要为 黑
return true;
}
KeyOfValue KOV; // 实例化仿函数对象, 为调用仿函数
// 树不为空, 就从根节点开始找位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (cur) {
if (KOV(data) > KOV(cur->_data)) { // 调用仿函数找key值 对比
// 插入数据大, 就向右子树找
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (KOV(data) < KOV(cur->_data)) {
// 插入数据小, 就向左子树找
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else {
// 树中已存在插入数据, 返回 false 插入失败
return false;
}
}
// 出循环之后, cur所在位置就是 新节点需要插入的位置
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_color = RED;
// parent 与 cur连接起来
if (KOV(data) > KOV(parent->_data)) {
// 数据大, 即新节点是父亲节点的右节点
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
else {
// 数据小, 即新节点是父亲节点的左节点
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
// 上面插入新节点时 已经记录了 cur 和 parent节点
while (parent && parent->_color == RED) {
// 父亲节点存在, 且父亲节点也为红色时
Node* grandFa = parent->_pParent; // 记录祖先节点
assert(grandFa); // 断言祖父节点存在
// 如果祖父节点不存在, 就说明 parent节点是树的根, 是不可能的 因为红黑树根不可能是红色的
if (parent == grandFa->_pLeft) {
// 父亲节点是祖先节点的左孩子
Node* uncle = grandFa->_pRight; // 记录叔叔节点
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) {
// 叔叔节点存在 且是红节点
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK; // 父亲节点 和 叔叔节点改为黑色
grandFa->_color = RED; // 祖父节点 改为红色
cur = grandFa; // 更新 grandFa节点为新的cur节点
parent = cur->_pParent; // 更新 新的parent节点
}
else {
// uncle为空 或 为黑时
if (cur == parent->_pLeft) {
// parent是grandFa的左孩子, cur是parent的左孩子, 即 直线的情况
rotateR(grandFa); // 将 祖先节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
parent->_color = BLACK; // 更新 parent节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
else {
// parent是grandFa的左孩子, cur是parent的右孩子, 即 折线的情况
rotateL(parent); // 先将 parent节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
rotateR(grandFa); // 再将 grandFa节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
cur->_color = BLACK; // 更新 cur节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
// 处理之后 结束循环
break;
}
}
else {
// 父亲节点是祖先节点的右孩子
Node* uncle = grandFa->_pLeft; // 记录叔叔节点
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) {
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandFa->_color = RED;
cur = grandFa;
parent = cur->_pParent;
}
else {
// uncle为空 或 为黑时
if (cur == parent->_pRight) {
// parent是grandFa的右孩子, cur是parent的右孩子, 即 直线的情况
rotateL(grandFa); // 将 祖先节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
parent->_color = BLACK; // 更新 parent节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
else {
// parent是grandFa的右孩子, cur是parent的左孩子, 即 折线的情况
rotateR(parent); // 先将 parent节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
rotateL(grandFa); // 再将 grandFa节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
cur->_color = BLACK; // 更新 cur节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
// 处理之后 结束循环
break;
}
}
}
_root->_color = BLACK; // 无论如何 最后更新根节点的颜色为黑
return true; // 插入完成, 返回true
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};除了对比key值需要使用仿函数之外, 没有什么需要注意的
然后就是 Set 和 Map的结构
上面分析过:
- Set 的模板参数只有一个 就是数据的类型, 内部调用红黑树, 模板传参就是
rb_tree<Key, Key> - Map 的模板参数有两个, 则 内部调用红黑树, 模板传参就是
rb_tree<Key, pair<Key, Value>>
而 由于需要兼容不同数据类型的指定方法的key值对比, 所以 添加一个仿函数用来取key值, 所以 set 和 map 的结构定义:
Set 的结构:
template<class Key> class Set { typedef Key key_type; typedef Key value_type; // 取key值的仿函数 struct SetKeyOfValue { const key_type& operator() (const value_type& key) { return key; } }; private: RB_Tree<key_type, key_type, SetKeyOfValue> _tree; };
Map 的结构:
template<class Key, class Value> class Map { typedef Key key_type; typedef pair<Key, Value> value_type; // pair<Key, Value>作为数据类型 // 取key值的仿函数 struct MapKeyOfValue { const key_type& operator() (const value_type& kv) { return kv.first; } }; private: RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, MapKeyOfValue> _tree; };
* 红黑树的迭代器
红黑树是二叉树, 每个单位是一个节点, 所以 红黑树迭代器 应该与 链表的迭代器相似 成员变量是红黑树的节点
template<class Type, class Ref, class Ptr> // 模板参数分别是 原类型, 引用类型, 指针类型
struct _RB_Tree_Iterator {
typedef RBTreeNode<Type> Node;
typedef _RB_Tree_Iterator<Typr, Ref, Ptr> Self;
_RB_Tree_Iterator(Node* node)
: _node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_data; // * 解引用 返回节点中的数据。返回值是引用类型 因为需要提供修改功能
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &_node->_data; // & 取地址 返回节点中数据的地址。返回值是指针类型
}
// 可能需要其他类访问, 所以设置为公有的
Node* _node;
};红黑树的迭代器重要的不是 结构, 最重要的是 ++ 和 -- 功能的逻辑和实现
迭代器 ++ — 的逻辑与实现
虽然 红黑树的迭代器本质上 就是树的某个节点, 但是 由于其整体结构是一棵树, 所以 ++ -- 的功能并不能像 链表那样直接 控制前后节点, 而是需要分析树的结构来进行功能的实现
set 和 map 的迭代器的 ++ 是 按照树的中序遍历顺序 移动的, 所以 rb_tree 的迭代器也需要按照此顺序
++
++ 操作需要将迭代器按照中序遍历的顺序移动, 怎么才能让指向当前节点位置的指针 去指向中序遍历中下一个节点的位置呢?
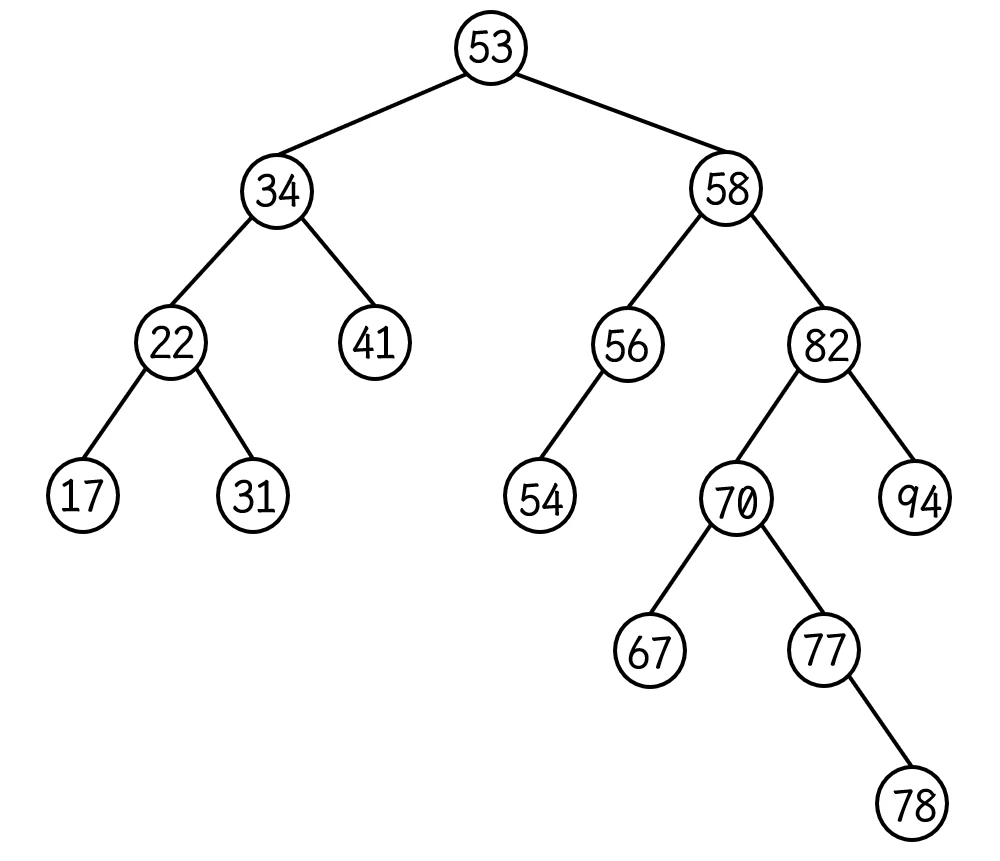
以一棵 二叉搜索树 为例:
此 红黑树的中序遍历是: 17 22 31 34 41 53 54 56 58 67 70 77 78 82 94
所以 迭代器实现的功能应该可以使 迭代器
++时 按照此顺序进行移动, 即:
- 17节点 —> 22节点(17节点的父亲, 17节点是其左孩子);
- 22节点 —> 31节点(22节点的右孩子);
- 31节点 —> 34节点(31节点的祖父);
- 34节点 —> 41节点(34节点的右孩子);
- 41节点 —> 53节点(41节点的祖父);
- 53节点 —> 54节点(53节点的右子树的最左孩子);
- 54节点 —> 56节点(54节点的父亲, 54节点是其左孩子);
- 56节点 —> 58节点(56节点的父亲, 56节点是其左孩子);
- 58节点 —> 67节点(58节点的右子树的最左孩子);
- 67节点 —> 70节点(67节点的父亲, 67节点是其左孩子);
- 70节点 —> 77节点(70节点的右孩子);
- 77节点 —> 78节点(77节点的右孩子);
- 78节点 —> 82节点(78节点的父亲的祖父);
- 82节点 —> 94节点(82节点的右孩子);
经过分析 可以发现:
当迭代器指向的节点 处于某节点的左孩子时, 迭代器
++, 迭代器就会指向父亲节点:17节点 —> 22节点(17节点的父亲, 17节点是其左孩子);
54节点 —> 56节点(54节点的父亲, 54节点是其左孩子);
56节点 —> 58节点(56节点的父亲, 56节点是其左孩子);
67节点 —> 70节点(67节点的父亲, 67节点是其左孩子);
这之中, 箭头 左边的节点 都是 右边节点的左孩子
当迭代器所指节点 拥有右子树时, 迭代器
++, 迭代器就会指向右子树的最左节点:22节点 —> 31节点(22节点的右孩子);
34节点 —> 41节点(34节点的右孩子);
53节点 —> 54节点(53节点的右子树的最左孩子);
58节点 —> 67节点(58节点的右子树的最左孩子);
70节点 —> 77节点(70节点的右孩子);
77节点 —> 78节点(77节点的右孩子);
82节点 —> 94节点(82节点的右孩子);
其中 31节点只是22节点的右孩子, 41节点只是34节点的右孩子…… 这是因为
右子树中只有一个节点, 就是此节点的右孩子, 也可以看作是 右子树的最左节点当迭代器指向的节点是某节点的右孩子时, 迭代器
++, 迭代器应该指向此节点祖先节点的路径上 第一个不为 某节点右孩子 的节点的父亲节点:31节点 —> 34节点(31节点的祖父);
31节点是22节点的右孩子, 所以向上找到 22节点, 22节点是34节点的左孩子, 即
22节点是 31节点祖先路径上的第一个不是右孩子的节点, 所以 迭代器需要 指向22节点的父亲节点41节点 —> 53节点(41节点的祖父);
78节点 —> 82节点(78节点的父亲的祖父);
78节点是77节点的右孩子, 向上找到 77节点, 77节点又是 70节点的右孩子, 继续向上找 70节点, 70节点是82节点的左孩子, 即
70节点是 78祖先路径上的第一个不是右孩子的节点, 所以 迭代器++ 需要指向70节点的父亲节点, 82节点但是 其实 1 和 3 是同一种情况:
此节点向上所在的路径上 第一个不是某节点右孩子的节点的父亲节点所以, 一共有两种情况
- 当 迭代器指向的节点 没有右孩子时, 即表示
需要找此节点向上路径上 第一个不是右孩子的节点的父亲节点- 当 迭代器指向的节点 存在右孩子时, 即表示
需要找此节点右子树的最左节点
根据上面的分析 就可以写出 红黑树迭代器++操作的相关代码:
Self& operator++() { // 无 int参数, 前置++
if (_node->_pRight == nullptr) { // 迭代器指向节点 没有 右孩子
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是右孩子的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pRight) { // 当父亲节点存在, 且cur节点还是其右孩子时 循环继续
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为右孩子的节点
_node = parent;
// 如果 迭代器++ 之前 指向的是树中最后一个节点, 则 执行上述代码之后
// cur会走到 整棵树的根节点, 而根节点的parent为空
// 所以 迭代器会为空
}
else { // 迭代器指向的节点 存在右子树
// 找右子树的最左节点
Node* farLeft = _node->_pRight;
while (farLeft->_pLeft) {
farLeft = farLeft->_pLeft;
}
_node = farLeft;
}
return *this; // 返回新的迭代器
}
Self operator++(int) { // 后置++
Self tmp(*this); // 拷贝此迭代器
++(*this); // 复用前置++
return tmp; // 返回++前 拷贝的迭代器
}—
++ 解决了之后, -- 就会非常的简单
与 ++ 的路径相反, 那么 操作与 ++ 也相反就可以
Self& operator--() // 无 int参数 前置--
{
if (_node->_left == nullptr) { // 当迭代器指向的节点 不存在左孩子 时
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是左孩子 的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pLeft) {
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为左孩子的节点
_node = parent;
}
else { // 迭代器指向节点 存在 左孩子时
// 找左子树的最右节点
Node* subRight = _node->_pLeft;
while (subRight->_pRight) {
subRight = subRight->_pRight;
}
_node = subRight;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
--(*this);
return tmp;
}迭代器相关代码
++ 和 -- 介绍过之后, 红黑树迭代器 最重要的内容就已经介绍完了, 剩下的就是补齐迭代器 相等和不等比较的功能
template<class Type, class Ref, class Ptr> // 模板参数分别是 原类型, 引用类型, 指针类型
struct _RB_Tree_Iterator {
typedef RBTreeNode<Type> Node;
typedef _RB_Tree_Iterator<Typr, Ref, Ptr> Self;
_RB_Tree_Iterator(Node* node)
: _node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_data; // * 解引用 返回节点中的数据。返回值是引用类型 因为需要提供修改功能
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &_node->_data; // & 取地址 返回节点中数据的地址。返回值是指针类型
}
Self& operator++() { // 无 int参数, 前置++
if (_node->_pRight == nullptr) { // 迭代器指向节点 没有 右孩子
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是右孩子的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pRight) { // 当父亲节点存在, 且cur节点还是其右孩子时 循环继续
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为右孩子的节点
_node = parent;
// 如果 迭代器++ 之前 指向的是树中最后一个节点, 则 执行上述代码之后
// cur会走到 整棵树的根节点, 而根节点的parent为空
// 所以 迭代器会为空
}
else { // 迭代器指向的节点 存在右子树
// 找右子树的最左节点
Node* farLeft = _node->_pRight;
while (farLeft->_pLeft) {
farLeft = farLeft->_pLeft;
}
_node = farLeft;
}
return *this; // 返回新的迭代器
}
Self& operator++(int) { // 后置++
Self tmp(*this); // 拷贝此迭代器
++(*this); // 复用前置++
return tmp; // 返回++前 拷贝的迭代器
}
Self& operator--() { // 无 int参数 前置--
if (_node->_left == nullptr) { // 当迭代器指向的节点 不存在左孩子 时
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是左孩子 的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pLeft) {
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为左孩子的节点
_node = parent;
}
else { // 迭代器指向节点 存在 左孩子时
// 找左子树的最右节点
Node* subRight = _node->_pLeft;
while (subRight->_pRight) {
subRight = subRight->_pRight;
}
_node = subRight;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
--(*this);
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& It) const {
return _node != It._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& It) const {
return _node == It._node;
}
// 可能需要其他类访问, 所以设置为公有的
Node* _node;
};底层 红黑树实现
迭代器分析完毕之后, 就可以简单 完善一下红黑树的接口了:
// 枚举常量, 表示 红 黑
enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode {
// RedBlackTreeNode 红黑树节点
RBTreeNode(const T& data = T())
: _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _color(RED) // 新节点默认为红节点
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _pLeft; // 节点左孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pRight; // 节点右孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _pParent; // 节点父亲节点
T _data; // 节点数据
Color _color; // 节点颜色
};
template<class Type, class Ref, class Ptr> // 模板参数分别是 原类型, 引用类型, 指针类型
struct _RB_Tree_Iterator {
typedef RBTreeNode<Type> Node;
typedef _RB_Tree_Iterator<Type, Ref, Ptr> Self;
_RB_Tree_Iterator(Node* node)
: _node(node)
{}
Ref operator*() {
return _node->_data; // * 解引用 返回节点中的数据。返回值是引用类型 因为需要提供修改功能
}
Ptr operator->() {
return &_node->_data; // -> 返回节点中数据的地址。返回值是指针类型
}
Self& operator++() { // 无 int参数, 前置++
if (_node->_pRight == nullptr) { // 迭代器指向节点 没有 右孩子
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是右孩子的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pRight) { // 当父亲节点存在, 且cur节点还是其右孩子时 循环继续
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为右孩子的节点
_node = parent;
// 如果 迭代器++ 之前 指向的是树中最后一个节点, 则 执行上述代码之后
// cur会走到 整棵树的根节点, 而根节点的parent为空
// 所以 迭代器会为空
}
else { // 迭代器指向的节点 存在右子树
// 找右子树的最左节点
Node* farLeft = _node->_pRight;
while (farLeft->_pLeft) {
farLeft = farLeft->_pLeft;
}
_node = farLeft;
}
return *this; // 返回新的迭代器
}
Self& operator++(int) { // 后置++
Self tmp(*this); // 拷贝此迭代器
++(*this); // 复用前置++
return tmp; // 返回++前 拷贝的迭代器
}
Self& operator--() { // 无 int参数 前置--
if (_node->_left == nullptr) { // 当迭代器指向的节点 不存在左孩子 时
// 需要从此节点向上找 第一个不是左孩子 的节点的父亲节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_pLeft) {
cur = cur->_pParent;
parent = parent->_pParent;
}
// 走到这里 cur节点就是 第一个不为左孩子的节点
_node = parent;
}
else { // 迭代器指向节点 存在 左孩子时
// 找左子树的最右节点
Node* subRight = _node->_pLeft;
while (subRight->_pRight) {
subRight = subRight->_pRight;
}
_node = subRight;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--(int) {
Self tmp(*this);
--(*this);
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& It) const {
return _node != It._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& It) const {
return _node == It._node;
}
// 可能需要其他类访问, 所以设置为公有的
Node* _node;
};
template<class Key, class Value_type, class KeyOfValue>
class RB_Tree {
typedef RBTreeNode<Value_type> Node; // 对节点类型进行typedef
public:
// 由于需要在类外使用 所以 typedef 为公共的
typedef _RB_Tree_Iterator<Value_type, Value_type&, Value_type*> iterator;
typedef _RB_Tree_Iterator<Value_type, const Value_type&, const Value_type*> const_iterator;
iterator begin() { // begin 取树的最左节点
Node* farLeft = _root;
while (farLeft && farLeft->_pLeft) {
// 判断 farLeft是否存在 是为了防止 树为空时 farLeft->_pLeft 访问使用空指针
farLeft = farLeft->_pLeft;
}
return iterator(farLeft);
}
iterator end() {
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const {
Node* farLeft = _root;
while (farLeft && farLeft->_pLeft) {
farLeft = farLeft->_pLeft;
}
return const_iterator(farLeft);
}
const_iterator end() const {
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
iterator find(const Key& key) {
// 查找节点 是按照 key 来找的
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfValue KOV;
while (cur) {
if (KOV(cur->_data) < key) {
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (KOV(cur->_data) > key) {
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else {
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return end(); // 走到这 就没有找到
}
// 插入数据之后 要返回新节点的迭代器 和 插入结果
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const Value_type& data) {
if (_root == nullptr) {
// 树为空时, 插入新节点
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_color = BLACK; // 根节点要为 黑
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
KeyOfValue KOV;
// 树不为空, 就从根节点开始找位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur->_pParent;
while (cur) {
if (KOV(data) > KOV(cur->_data)) {
// 插入数据大, 就向右子树找
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pRight;
}
else if (KOV(data) < KOV(cur->_data)) {
// 插入数据小, 就向左子树找
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_pLeft;
}
else {
// 树中已存在插入数据, 返回 false 插入失败
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
// 出循环之后, cur所在位置就是 新节点需要插入的位置
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newNode = cur; // 记录新节点位置 以返回
cur->_color = RED;
// parent 与 cur连接起来
if (KOV(data) > KOV(parent->_data)) {
// 数据大, 即新节点是父亲节点的右节点
parent->_pRight = cur;
}
else {
// 数据小, 即新节点是父亲节点的左节点
parent->_pLeft = cur;
}
cur->_pParent = parent;
// 上面插入新节点时 已经记录了 cur 和 parent节点
while (parent && parent->_color == RED) {
// 父亲节点存在, 且父亲节点也为红色时
Node* grandFa = parent->_pParent; // 记录祖先节点
assert(grandFa); // 断言祖父节点存在
// 如果祖父节点不存在, 就说明 parent节点是树的根, 是不可能的 因为红黑树根不可能是红色的
if (parent == grandFa->_pLeft) {
// 父亲节点是祖先节点的左孩子
Node* uncle = grandFa->_pRight; // 记录叔叔节点
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) {
// 叔叔节点存在 且是红节点
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK; // 父亲节点 和 叔叔节点改为黑色
grandFa->_color = RED; // 祖父节点 改为红色
cur = grandFa; // 更新 grandFa节点为新的cur节点
parent = cur->_pParent; // 更新 新的parent节点
}
else {
// uncle为空 或 为黑时
if (cur == parent->_pLeft) {
// parent是grandFa的左孩子, cur是parent的左孩子, 即 直线的情况
rotateR(grandFa); // 将 祖先节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
parent->_color = BLACK; // 更新 parent节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
else {
// parent是grandFa的左孩子, cur是parent的右孩子, 即 折线的情况
rotateL(parent); // 先将 parent节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
rotateR(grandFa); // 再将 grandFa节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
cur->_color = BLACK; // 更新 cur节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
// 处理之后 结束循环
break;
}
}
else {
// 父亲节点是祖先节点的右孩子
Node* uncle = grandFa->_pLeft; // 记录叔叔节点
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED) {
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandFa->_color = RED;
cur = grandFa;
parent = cur->_pParent;
}
else {
// uncle为空 或 为黑时
if (cur == parent->_pRight) {
// parent是grandFa的右孩子, cur是parent的右孩子, 即 直线的情况
rotateL(grandFa); // 将 祖先节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
parent->_color = BLACK; // 更新 parent节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
else {
// parent是grandFa的右孩子, cur是parent的左孩子, 即 折线的情况
rotateR(parent); // 先将 parent节点作为rotateR的parent, 右单旋
rotateL(grandFa); // 再将 grandFa节点作为rotateL的parent, 左单旋
cur->_color = BLACK; // 更新 cur节点颜色为黑
grandFa->_color = RED; // 更新 grandFa节点颜色为红
}
// 处理之后 结束循环
break;
}
}
}
_root->_color = BLACK; // 无论如何 最后更新根节点的颜色为黑
return make_pair(iterator(newNode), true);
}
private:
void rotateL(Node* parent) {
Node* subR = parent->_pRight;
Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;
parent->_pRight = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_pParent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_pParent;
subR->_pLeft = parent;
parent->_pParent = subR;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subR;
_root->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (parent == ppNode->_pLeft)
ppNode->_pLeft = subR;
else
ppNode->_pRight = subR;
subR->_pParent = ppNode;
}
}
void rotateR(Node* parent) {
Node* subL = parent->_pLeft;
Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;
parent->_pLeft = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_pParent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_pParent;
subL->_pRight = parent;
parent->_pParent = subL;
if (parent == _root) {
_root = subL;
_root->_pParent = nullptr;
}
else {
if (parent == ppNode->_pLeft)
ppNode->_pLeft = subL;
else
ppNode->_pRight = subL;
subL->_pParent = ppNode;
}
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};set 和 map 的封装
set 和 map 是以红黑树为底层封装起来的, 上面已经实现了 红黑树的一些简单的接口的相关代码, 所以 set和map 的封装 可以直接调用 红黑树的接口进行实现:
set 的封装:
template<class Key> class set { typedef Key key_type; typedef Key value_type; // 取key值的仿函数 struct SetKeyOfValue { const key_type& operator() (const value_type& key) { return key; } }; public: // 封装红黑树的迭代器 typedef typename RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, SetKeyOfValue>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, SetKeyOfValue>::const_iterator const_iterator; // 由于 迭代器需要在类外定义 所以需要typedef为 公用的 iterator begin() const { return _tree.begin(); } iterator end() const { return _tree.end(); } pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& v) { auto ret = _tree.insert(v); return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(ret.first._node), ret.second); } iterator find(const key_type& key) { return _tree.find(key); } private: RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, SetKeyOfValue> _tree; };
map 的封装:
template<class Key, class Value> class map { typedef Key key_type; typedef pair<Key, Value> value_type; // pair<Key, Value>作为数据类型 // 取key值的仿函数 struct MapKeyOfValue { const key_type& operator() (const value_type& kv) { return kv.first; } }; public: // 封装红黑树的迭代器 typedef typename RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, MapKeyOfValue>::iterator iterator; typedef typename RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, MapKeyOfValue>::const_iterator const_iterator; iterator begin() { return _tree.begin(); } iterator end() { return _tree.end(); } pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& kv) { return _tree.insert(kv); } iterator find(const key_type& k) { return _tree.find(k); } Value& operator[](const key_type& k) { pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(k, Value())); // 调用map的插入 return ret.first->second; // ret 的 first 是 map的迭代器 // 红黑树中实现过 迭代器的 -> 操作是取 迭代器所指向节点的数据 // map的数据是 pair<key_type, value_type> 类型的 // 所以 ret.first->second 即为结果 } private: RB_Tree<key_type, value_type, MapKeyOfValue> _tree; };
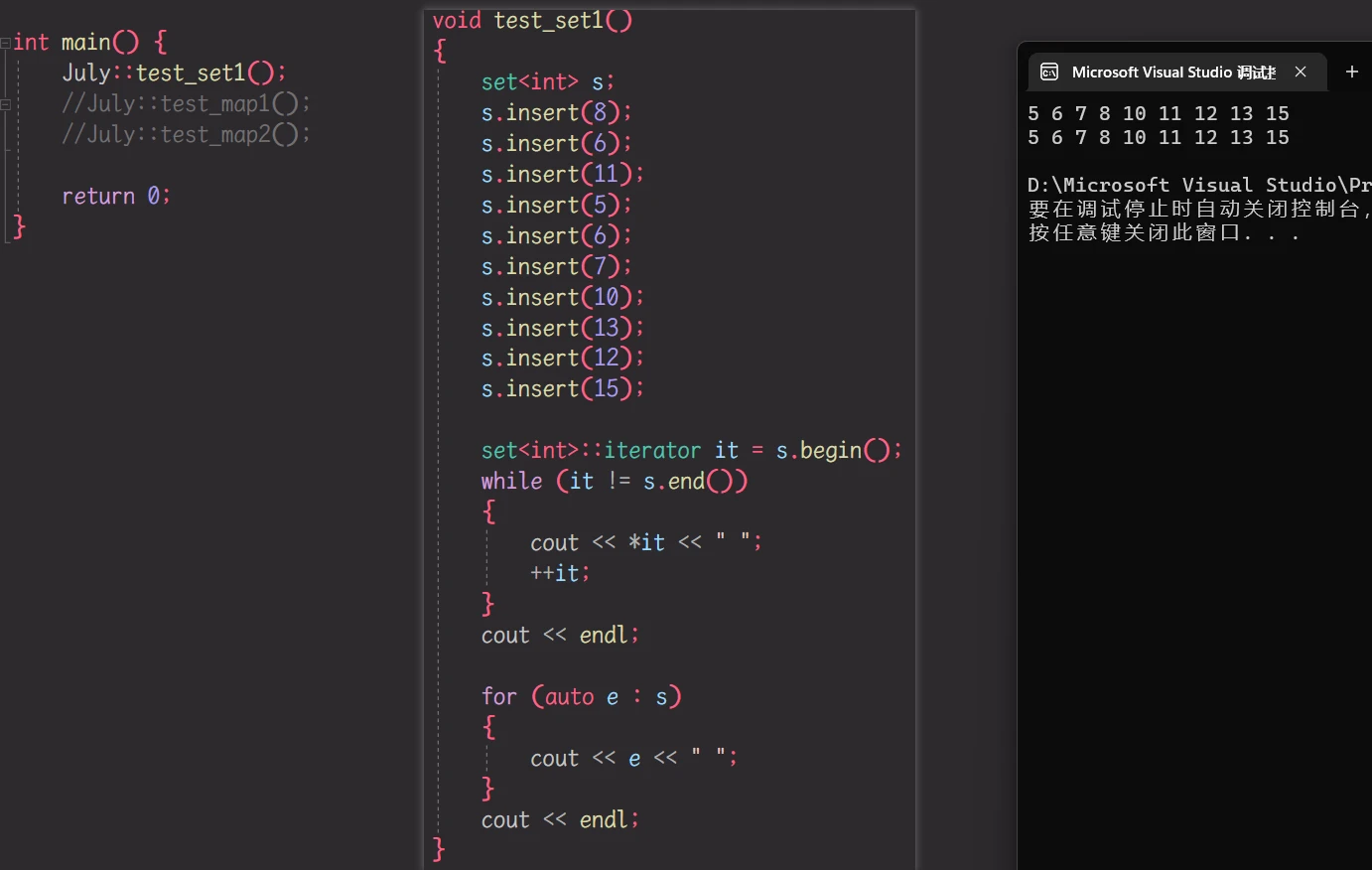
封装完成之后, 就可以进行测试:
测试 set:
测试 map:
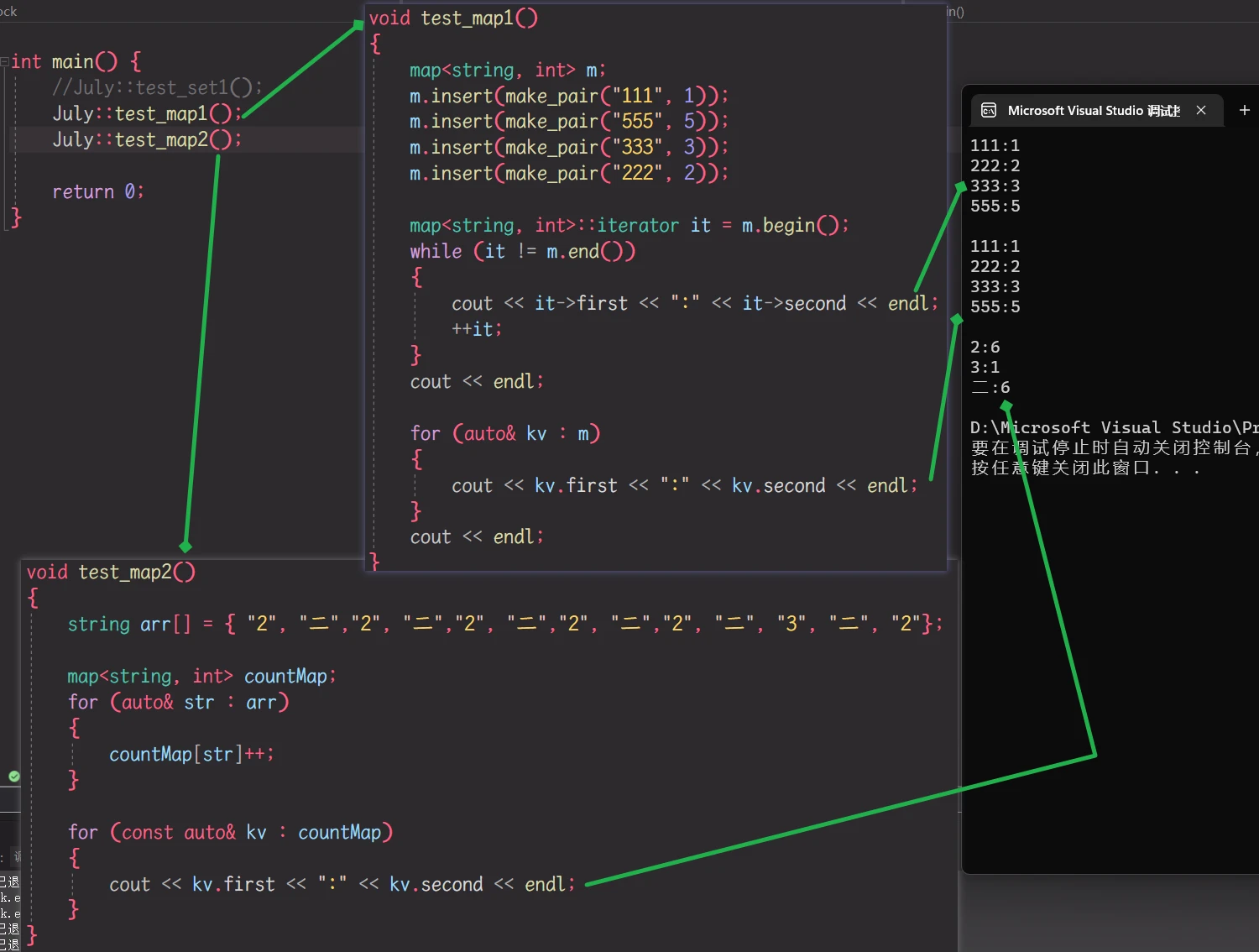
![[C++-STL] set和map容器的模拟实现](https://dxyt-july-image.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/202306251814109.webp)